In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, small businesses are increasingly turning to cloud computing to streamline operations, enhance flexibility, and boost overall efficiency. If you find yourself scratching your head at the mention of “cloud computing,” fear not! This guide aims to demystify the cloud and show you how it can be a game-changer for your small business.
What is Cloud Computing?
At its core, cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—such as storage, processing power, and software—over the internet. Instead of relying on a local server or computer infrastructure, you can access these resources remotely, anytime, anywhere.
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing for Small Businesses
1. Cost-Efficiency – Traditional IT setups often require significant upfront investments in hardware and maintenance. With cloud computing, you can say goodbye to hefty capital expenses. Cloud services operate on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing you to scale resources based on your needs and only pay for what you use.
2. Flexibility and Scalability – Small businesses evolve, and so should your IT infrastructure. Cloud services offer the flexibility to scale up or down based on your business demands. Whether you’re experiencing rapid growth or a seasonal slowdown, the cloud allows you to adapt without the headache of hardware upgrades.
3. Accessibility – One of the cloud’s most significant advantages is accessibility. Your data and applications are no longer tied to a specific device or location. With an internet connection, you and your team can collaborate seamlessly, whether you’re in the office, at home, or on the go.
4. Enhanced Collaboration – Cloud-based tools facilitate real-time collaboration among team members. Shared documents, calendars, and project management tools ensure that everyone is on the same page, fostering teamwork and productivity.
Types of Cloud Services

Let’s delve deeper into the 3 main types of cloud services:
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, allowing businesses to rent IT infrastructure on a pay-as-you-go basis. This includes virtual machines, storage, and networking components.
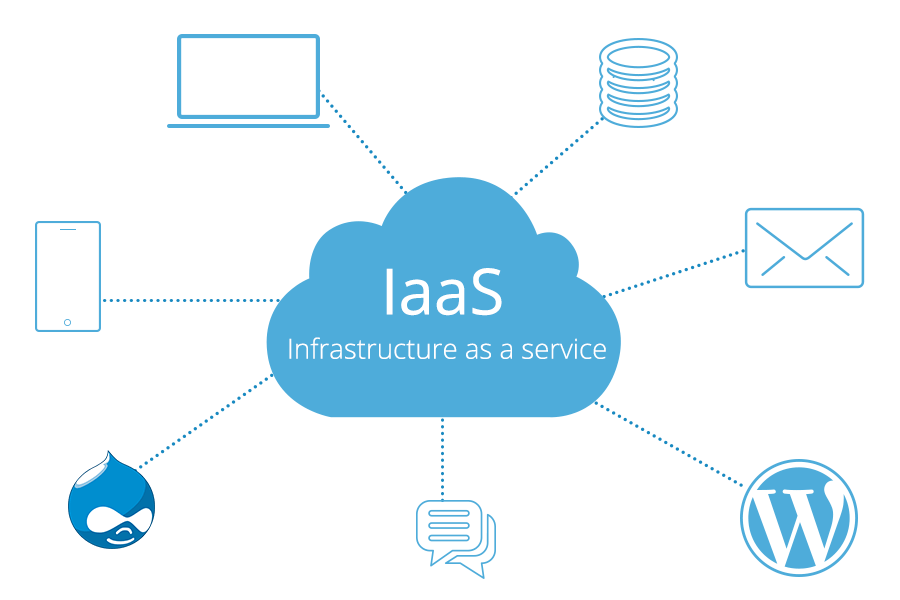
Use Cases:
- Scalable Computing Power: Businesses can scale their computing resources up or down based on demand, making it ideal for variable workloads.
- Storage Solutions: IaaS is commonly used for data storage and backup solutions without the need for physical hardware.
- Network Infrastructure: Virtualized networking components enable businesses to manage their network infrastructure more efficiently.
Examples of IaaS Providers:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a platform that allows businesses to develop, run, and manage applications without dealing with the complexities of underlying infrastructure. It includes tools and services for application development, such as databases, middleware, and development frameworks.
Use Cases:
- Application Development: Developers can focus on coding without worrying about the underlying infrastructure, streamlining the development process.
- Collaborative Development: PaaS facilitates collaboration among development teams, making it easier to work on projects together.
Examples of PaaS Providers:
- Heroku
- Microsoft Azure App Service
- Google App Engine
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Instead of purchasing and installing software on individual devices, users can access the application through a web browser.
Use Cases:
- Productivity Tools: SaaS provides access to a wide range of productivity tools, including email, collaboration software, and office suites.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Many CRM tools are offered as SaaS, enabling businesses to manage customer relationships more effectively.
Examples of SaaS Providers:
- Microsoft 365 (formerly Office 365)
- Salesforce
- Dropbox
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business:
When selecting a cloud service model, consider your business needs, budget constraints, and technical requirements. Some businesses may benefit from a combination of these services, known as the hybrid cloud, which integrates on-premises infrastructure with cloud services.
By understanding the distinctions between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, small business owners can make informed decisions about how to leverage cloud computing to optimize their operations and drive success.
Security Considerations
While the cloud offers numerous benefits, it’s crucial to address security concerns. Choose reputable cloud service providers that implement robust security measures, including data encryption, regular audits, and multi-factor authentication.
Getting Started
1. Assess Your Needs: Identify the areas where cloud computing can enhance your business processes.
2. Choose the Right Service Model: Depending on your requirements, opt for IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS.
3. Select a Reliable Provider: Research and choose a reputable cloud service provider with a track record of security and reliability.
4. Migrate Gradually: Consider migrating to the cloud gradually, starting with non-critical applications and data.
5. Educate Your Team: Ensure your team is familiar with cloud tools and best practices to maximize the benefits of your cloud migration.
Overcoming Common Concerns
As you embark on your cloud computing journey, it’s natural to have concerns about data security, privacy, and the learning curve associated with adopting new technologies. Let’s address these apprehensions:
1. Data Security
Security is a top priority for cloud service providers. They invest heavily in advanced security measures, including encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems. Regular security audits and compliance certifications ensure that your data is handled with the utmost care. Additionally, by centralizing data in secure data centers, the cloud often provides a more robust security infrastructure than many small businesses can afford on their own.
2. Privacy and Compliance
Cloud providers adhere to strict privacy standards and regulatory compliance. When choosing a cloud service, verify that they comply with relevant regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or any industry-specific requirements. Many providers also offer tools to help you manage compliance, giving you peace of mind regarding the legal aspects of your data.
3. Learning Curve
Adopting new technology can be daunting, especially for small businesses with limited IT resources. However, most cloud services are designed with user-friendly interfaces, and many providers offer extensive documentation and support. Training your team on the basics of cloud usage can quickly alleviate concerns and pave the way for a smoother transition.
To illustrate the tangible benefits of cloud computing, let’s look at a few real-world examples:
1. Cost Savings for Start-ups
Imagine you’re a start-up with limited funds. Instead of investing in expensive servers and infrastructure, you can use cloud services to scale your operations as you grow. This cost-effective approach allows you to allocate resources where they’re needed most—developing and expanding your business.
2. Remote Work Revolution
In the age of remote work, the cloud has become indispensable. Small businesses can leverage cloud-based collaboration tools to enable seamless communication and project management among remote teams. This flexibility not only boosts productivity but also attracts top talent, regardless of geographical constraints.
3. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Traditional disaster recovery plans can be complex and costly. With the cloud, your data is backed up automatically, and in the event of a disruption, you can quickly recover and resume operations. This ensures minimal downtime, allowing your small business to weather unexpected challenges more effectively.
The Future of Small Business in the Cloud
The future of small businesses lies in the clouds, a digital frontier reshaping the entrepreneurial landscape. Cloud computing is the catalyst for agility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. It empowers small businesses to compete on a global scale, breaking down geographical barriers. The cloud fosters innovation, allowing entrepreneurs to focus on growth rather than IT complexities. Enhanced collaboration and remote work capabilities are becoming the norm, revolutionizing traditional business structures. As technology advances, the cloud will continue to be the cornerstone of small business success, offering unparalleled flexibility and opportunities for those ready to embrace the digital horizon.
In Conclusion
Cloud computing is not just for tech giants; it’s a powerful tool that can propel small businesses forward. By embracing the cloud, you’ll not only streamline your operations but also gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic business landscape. Take the leap into the cloud, and watch your small business soar to new heights!
In conclusion, the cloud is not just a tool for large enterprises; it’s a transformative force that can elevate small businesses to new heights. By understanding the basics, overcoming concerns, and learning from real-world examples, you can harness the power of cloud computing to propel your small business into a future of growth and success.